What is hedging in option trading
By OnePunchAlgo in Option Trading Posted October 13, 2025
In the world of financial markets, every trader enters with the same hope: to generate profit. But as experience grows, that hope evolves into something deeper and far more strategic. The traders who consistently survive and thrive aren’t the ones who chase the biggest wins; they are the ones who understand that protection is profit.
Markets are dynamic, unpredictable, and often unforgiving. Price can rise, collapse, or move sideways without warning. Indicators lag, news shocks disrupt trends, and volatility can erase months of gains in minutes. This is why professional traders don’t approach markets as a sequence of victories. They treat it as a mathematical landscape, one where every decision balances risk, reward, exposure, and probability.
Every potential profit carries uncertainty. Every position exposes you to market forces. But the best traders don’t run from that risk; they engineer it. They shape their exposure the way an architect shapes stress in a structure, reinforcing weak points and redirecting pressure. They don’t avoid risk; they control it, refine it, and convert it into a strategic advantage.
This is where hedging comes into play.
Hedging is not a defensive move; it is a structural tool. It is the mechanism through which traders protect capital, smooth volatility, and stay alive during adverse conditions. In the elite layers of finance, hedging is considered the silent guardian of every serious portfolio. This technique ensures longevity in a field where survival itself becomes a competitive edge.
And in the realm of options trading, hedging transforms into both an art and a science. Options allow you to reshape risk more precisely than any other financial instrument. They can reduce exposure, offset losses, create asymmetric payoffs, or even convert a losing trade into a profitable one under the right circumstances.
But behind the simple definition lies a more profound truth:
Hedging is the discipline of staying in the game long enough to win.
It’s not about eliminating risk, because eliminating risk would also eliminate opportunity. It’s about controlling risk intelligently, so you can participate in the upside without being destroyed by the downside.
It’s where market psychology meets probability,
– where mathematics meets strategy,
– and where precision meets protection.
This guide will walk you through the full ecosystem of hedging within option trading. You’ll move from foundational concepts, perfect for beginners, to advanced, structural strategies used by professional traders and institutions.
1. From Market Chaos to Strategic Control: The Role of Hedging
Imagine two traders facing the same market drop.
– One panics, sells everything, and locks in losses.
– The other stays calm, knowing their downside is already protected.
That calmness comes from a hedge, a strategic layer of defense built into their trading plan.
What Is Hedging?
In the simplest sense, hedging means creating an offsetting position that reduces or neutralizes potential loss from another position. It’s like buying insurance; you pay a small premium to ensure that, if things go wrong, you’re not wiped out.
- When the market moves against you, the hedge increases in value.
- When the market moves in your favor, the hedge loses small value, but your main position gains more.
Professionals use hedging to:
- Maintain emotional stability
- Hold long-term positions during volatility
- Smooth out portfolio performance
- Survive market storms without panic
In the context of option trading, hedging is not only about safety, but it’s also about control. It allows traders to navigate uncertain markets, to profit from volatility, and to hold strong positions without emotional interference. But before we get into hedging, let’s go back to where it all begins: understanding what an option really is.
2. What Is Option Trading? A Foundation for Every Hedge
An option is a financial contract that gives the holder the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an underlying asset, such as a stock, ETF, index, future, currency, or commodity, at a specific price (called the strike price) before or on a set expiration date.
In simple terms, options are like reservations:
- You pay a premium to secure the right to buy or sell at a certain price.
- You can choose to exercise the option if the market moves in your favor.
- Or, you can let it expire if it doesn’t — losing only the premium paid.
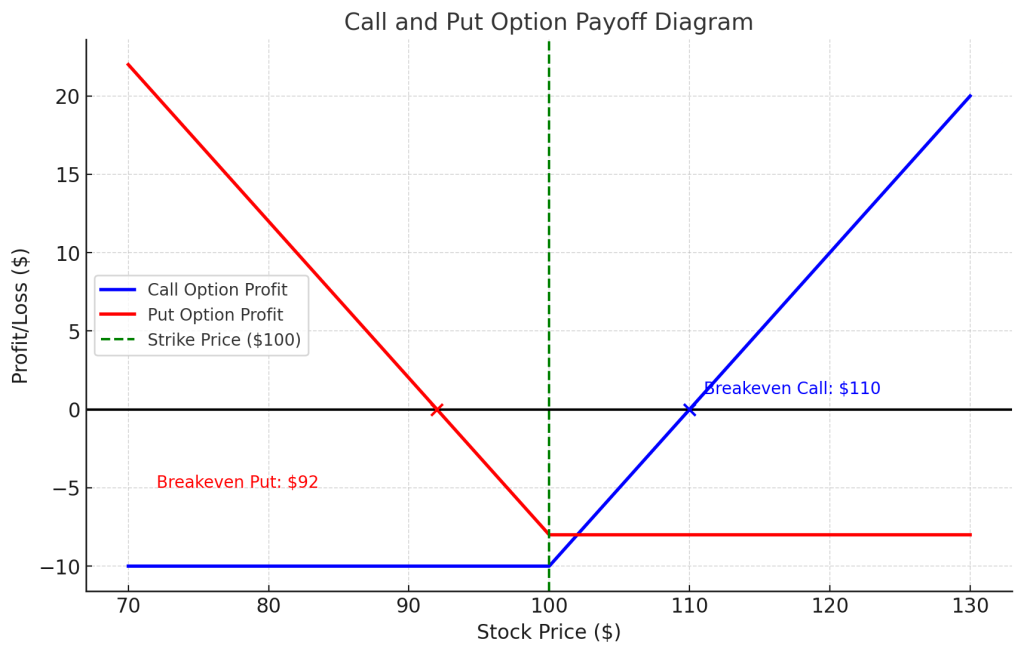
There are two main types of options:
- Call Options – The right to buy the underlying asset.
- Put Options – The right to sell the underlying asset.
Each option contract typically represents 100 shares of the underlying asset in U.S. markets.
Example:
You buy a Call Option for Apple (AAPL) with:
- Strike price: $180
- Premium: $5
- Expiration: 30 days
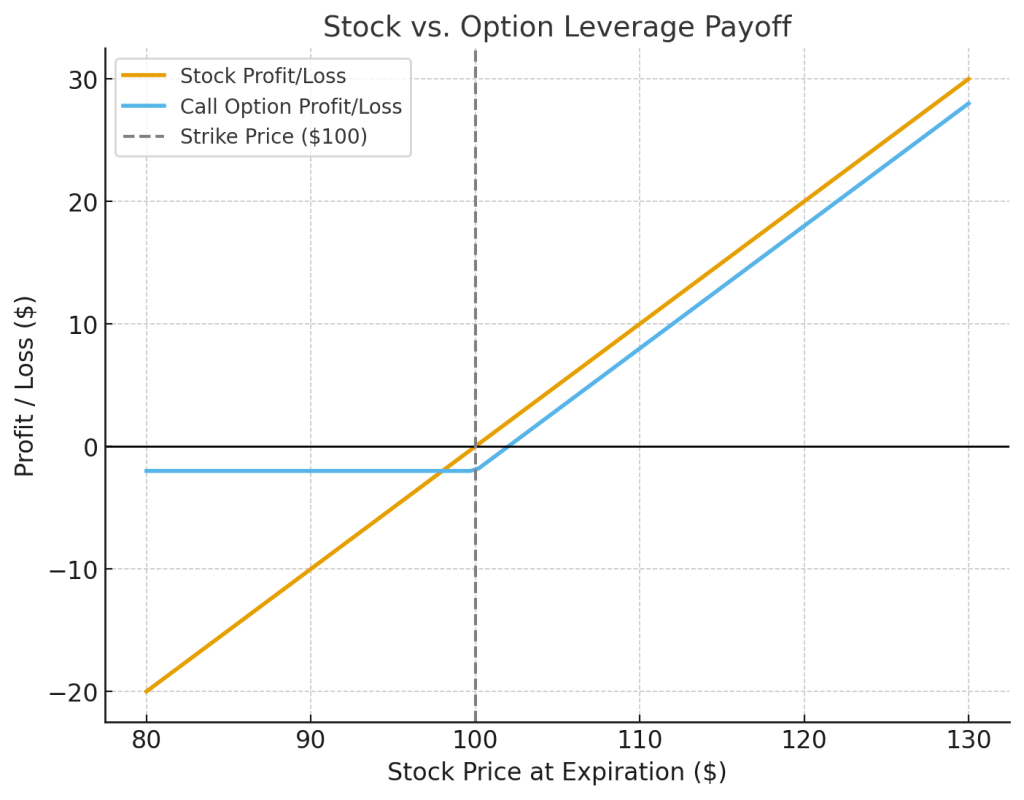
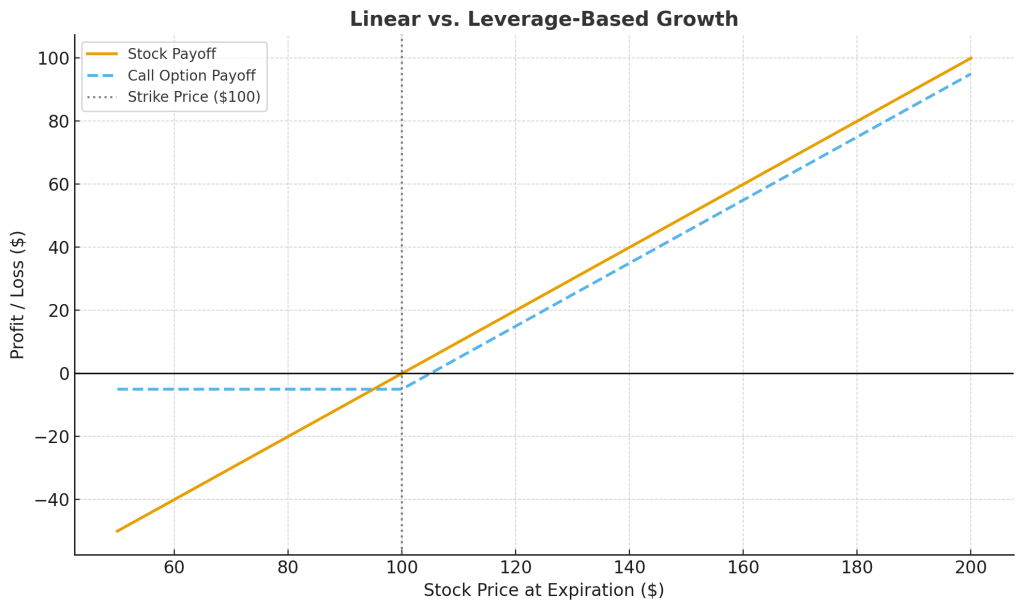
If Apple’s market price rises to $190, your call becomes profitable, you can buy shares for $180 and sell them for $190, gaining $10 per share (minus the $5 premium). That’s a $500 profit on a $500 investment; a 100% return.
This is the power of leverage, one of the most attractive features of option trading.
But the same leverage that amplifies profits can also magnify losses. And that’s why hedging becomes essential.
3. Why Hedging Matters: The Philosophy of Controlled Risk
In trading, risk cannot be eliminated; it can only be managed. Professional traders understand that success isn’t about avoiding losses; it’s about limiting them while letting gains grow.
That’s the heart of hedging, using strategic positions to control exposure.
Options are unique among financial instruments because they offer asymmetric risk: limited downside and unlimited upside. This makes them ideal for precision hedging, where every dollar spent is a calculated trade-off between protection and opportunity. When you hedge with options, you’re essentially buying time and stability in a market that’s constantly changing. You gain:
Here’s why professional traders and institutions rely on option hedging:
- Capital Efficiency: Options require less capital than selling or buying large amounts of stock.
- Flexibility: You can tailor hedges for duration, volatility, or specific price levels.
- Controlled Exposure: Adjust your delta, gamma, or vega exposure without altering your core position.
- Portfolio Stability: Reduce drawdowns during market turbulence while keeping positions open for recovery.
- Psychological Clarity: Knowing your downside risk frees you from emotional decision-making under pressure.
- Protection from sharp adverse moves.
- Confidence to follow your plan instead of reacting emotionally.
Without hedging, you’re gambling. With hedging, you’re operating a business, structured, calculated, and sustainable.
Why Options Are the Perfect Hedging Tool
- Low cost for high protection (buy a put instead of selling the entire stock)
- Customizable (choose your strike, duration, delta, and risk profile)
- Defined risk before entering the trade
- Profit-retention while maintaining upside exposure
Hedging is not about predicting the market. It’s about preparing for all possible outcomes.
4. Key Hedging Strategies Using Options
At its core, hedging in option trading means using options contracts to offset the risk of an existing position, whether it’s in stocks, ETFs, or futures. Let’s break down the most widely used hedging structures that traders apply using calls and puts.
A. Protective Put – The Classic Insurance Strategy
A Protective Put is one of the most straightforward hedges. It’s used when you own a stock but fear a short-term decline.
How it works
- You own the stock.
- You buy a put option at a price below its current price.
If the stock drops, the put increases in value, offsetting the loss.
Why traders use it
- Unlimited upside on the stock
- Limited downside thanks to the put
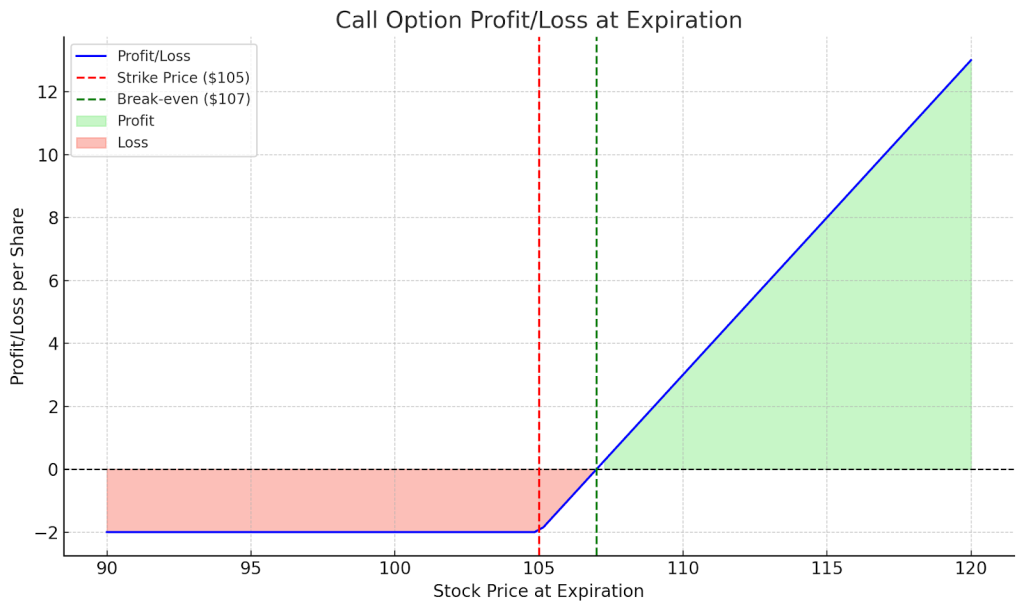
Payoff Logic (Graph Description)
Stock Price ↓ → Put Value ↑ → Loss is capped
Your total P/L line flattens below the strike price, creating a safety floor.
Example:
You own 100 shares of Tesla (TSLA) at $250 each. You’re optimistic in the long term but fear a short-term drop.
You buy a Put Option:
- Strike Price: $240
- Premium: $3 ($300 total)
- Expiration: 30 days
If TSLA drops to $220, your stock loses $3,000, but your put option gains $2,000 in intrinsic value. Your net loss is only $1,000 (plus the $300 cost of the put).
That’s hedging in action, converting an open-ended risk into a controlled, limited risk position.

B. Covered Call – Income-Based Hedge
A Covered Call is another popular hedging approach, but instead of pure protection, it focuses on income generation.
How it works
- You own the stock.
- You sell a call option above the current price.
- You collect premium (income).
If the stock stays below the strike, you keep the income. If it rises above, your profit is capped.
Why traders use it
- Generates passive income
- Reduces cost basis
- Offers partial downside protection
Payoff Logic
Profit rises steadily until the strike price, then flattens (capped upside).
Example:
You own 100 shares of Microsoft (MSFT) at $400. You believe it will stay between $390 and $410 next month.
You sell a Call Option with:
- Strike: $410
- Premium: $4
If MSFT stays below $410, you keep the $400 premium, which is a 1% income per month. If it rises above $410, you sell the stock at that price, locking in a $10-per-share gain plus the premium.
This is another form of hedging, protecting yourself through income generation that offsets potential losses from sideways or minor declines.

C. Collar Strategy – The Balanced Risk Framework
A collar combines the protective put and the covered call. It’s designed to lock in a profit range or limit losses and gains within a defined corridor, creating a near-perfect risk-balanced hedge. This approach is favored by institutional investors who prefer steady performance over speculation.
Combines both:
- Buy a protective put
- Sell a call to finance the put
Often becomes a zero-cost collar (no net cost).
Why traders use it
- Downside is protected
- Upside is capped
- Perfect for high volatility or protecting significant gains
Payoff Logic
Flat below the put strike → rising middle zone → flat above call strike.
This strategy creates a controlled profit zone and is especially used by fund managers to maintain stable returns.

5. The Science Behind Hedging: The Greeks
To master hedging, you must understand the Greeks, mathematical measures of how an option’s price reacts to changes in the market.
| Greek | Meaning | Role in Hedging |
| Delta (Δ) | Sensitivity to price changes | Used to measure how much your hedge offsets the underlying move. |
| Gamma (Γ) | Rate of change of delta | Shows how stable your hedge is as the price changes. |
| Theta (Θ) | Time decay | Essential for knowing how long your hedge remains cost-effective. |
| Vega (ν) | Sensitivity to volatility | Determines how hedges behave when volatility spikes. |
A delta-neutral portfolio (where total delta = 0) is one where gains and losses balance regardless of small price moves; this is the holy grail of professional hedging.
6. Hedging and Profit: The Paradox of Success
Many beginners think hedging reduces profit potential, but in reality, it enables sustainable profitability.
Why? Because trading is not about hitting home runs, it’s about preserving capital long enough to compound it.
A trader who loses 50% of their account must gain 100% just to recover. But a trader who limits losses to 10% can rebound easily and grow faster over time. That’s why the most successful traders in the world, from institutional desks to proprietary firms, prioritize risk-adjusted returns, not raw profit. They measure performance by consistency, not excitement.
7. Practical Hedging Scenarios for New Traders
Here’s how beginners can apply hedging concepts in real trading environments:
- If you hold a long-term stock portfolio, buy puts on indexes like SPY or QQQ during volatile months.
- If you trade short-term options, use stop-losses and calendar spreads to hedge theta decay.
- If you trade directionally, combine vertical spreads (such as bull call spreads) to limit risk while maintaining leverage.
- If you hold volatile assets like crypto or small caps, use collars to lock in profits after strong rallies.
The key is to build a system, not to react randomly. Every hedge should serve a defined purpose: protection, time extension, or volatility control.
8. The Psychology of Hedging: Calm in the Storm
The best traders aren’t the ones who trade without fear, nor the ones who try to predict every move of the market; they’re the ones who are prepared for every outcome. Hedging gives traders that preparation. It creates emotional stability in environments where others panic, turning chaos into clarity. With a proper hedge in place, fear is replaced by process, uncertainty becomes manageable, and the trader can focus on disciplined execution rather than emotional reaction.
In essence, hedging is the bridge between emotional control and financial discipline: the core architecture of every consistently profitable trader’s mindset. It is where psychology meets mathematics, where intuition aligns with logic, and where disciplined risk management becomes the foundation for long-term success.
9. Common Mistakes Traders Make When Hedging
Even experienced traders misuse hedges. Some common pitfalls include:
- Over-hedging: Spending too much on protection, eating into profits.
- Ignoring volatility: Buying puts when IV (implied volatility) is already high.
- Poor timing: Hedging too late after the market has already dropped.
- Misaligned expirations: Choosing hedges that don’t match the risk horizon.
- Not adjusting hedges as prices evolve.
Hedging is a dynamic process, not a one-time action.
The golden rule: hedge before you need it, not after.
10. How Beginners Should Use Hedging
If you hold long-term stocks
→ Buy protective puts during earnings, elections, or volatility spikes.
If you trade options short-term
→ Use spread strategies (vertical/call spreads) to limit risk.
If you hold volatile assets
→ Use collars to lock in profits after large moves.
If you want stability
→ Use covered calls to reduce cost basis steadily.
Every hedge must have a purpose: Protection, volatility control, or time extension.
11. The Role of Technology and Modern Tools
In today’s world, traders don’t hedge blindly. They use advanced algorithms, volatility models, and chart-based frameworks to find reaction zones, momentum traps, and price reversals before they happen.
Platforms like OnePunch ALGO build educational ecosystems around such systems, helping traders visualize structure-based trading and identify high-probability zones across assets such as SPX, QQQ, and futures.
These aren’t “guarantee tools”; they’re supporting frameworks that empower traders to combine knowledge with disciplined execution.
A perfect example of this structured, data-driven approach can be seen in this market breakdown, where SPY and QQQ are analyzed through order flow, delta volume shifts, and reaction zones during the FOMC volatility spike.
Conclusion: Hedging – The Signature of a Professional Trader
In the world of financial markets, profit does not reward prediction; it rewards preparation. Option trading gives you an extraordinary advantage: the ability to shape risk, not simply react to it. And hedging is the centerpiece of that control.
Hedging transforms uncertainty into structure, emotion into logic, and volatility into opportunity. It is the discipline that keeps new traders grounded and the mechanism that gives experienced traders the longevity to compound for years, not days.
Professional traders are not defined by fearlessness; they are defined by their ability to manage exposure with precision. Whether you trade a small account or a diversified portfolio, hedging is not a restriction. It is freedom.
Freedom to stay in winning trades longer.
Freedom to survive market storms.
Freedom to grow with consistency instead of chaos.
And as you continue mastering this craft, you’ll find that growth accelerates when education, community, and structured tools support your evolution.
That is where resources like the OnePunch ALGO Academy and the OnePunch ALGO YouTube Channel become powerful companions. They offer structured systems, educational breakdowns, live market perspectives, and practical guidance, tools designed to enhance your decision-making, sharpen your strategy, and help you trade with clarity rather than emotion. These are the types of resources traders rely on when they’re serious about developing skill, not shortcuts. If hedging is the signature of a professional trader, continuous education is the fuel that keeps that professionalism alive.
Explore the Academy. Watch the channel. Strengthen your craft.
Your success is built on the choices you make, and aligning yourself with the right knowledge is the first step toward mastering the markets with confidence and precision.
READ MORE